Delving into the realm of materials science, we present the FCC Element 3 Study Guide PDF, an invaluable resource that unravels the intricacies of FCC element 3, its properties, applications, and more. Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into the world of face-centered cubic crystal structures and their remarkable impact on various industries.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of FCC element 3, encompassing its atomic structure, physical and chemical properties, and the relationship between its crystal structure and its unique characteristics. By understanding these fundamental aspects, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the role of FCC element 3 in shaping our technological advancements.
Introduction to FCC Element 3

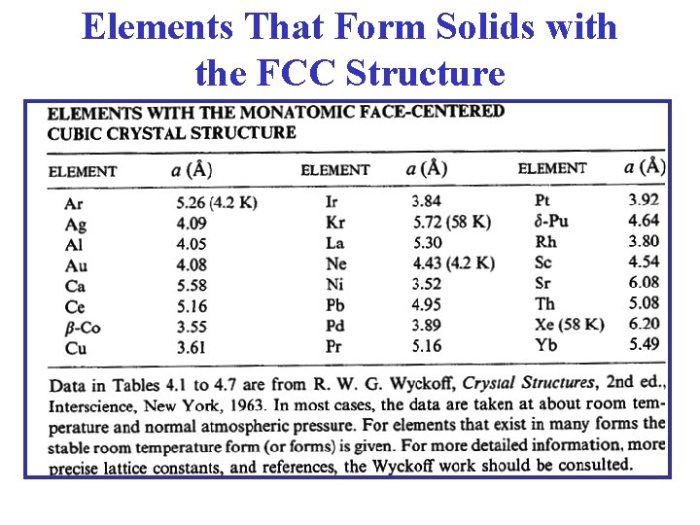
Face-centered cubic (FCC) is a crystal structure where atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with atoms at each corner and in the center of each face of the cube.
The FCC structure is one of the most common crystal structures found in metals. It is a very stable structure, which is why it is found in many different types of materials.
Arrangement of Atoms in an FCC Lattice
In an FCC lattice, the atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with atoms at each corner and in the center of each face of the cube.
The FCC lattice can be visualized as a cube with atoms at each corner and in the center of each face. The atoms at the corners of the cube are shared by eight neighboring cubes, while the atoms in the center of each face are shared by two neighboring cubes.
Properties of FCC Element 3: Fcc Element 3 Study Guide Pdf

FCC element 3, with its unique face-centered cubic crystal structure, exhibits distinct physical and chemical properties that set it apart from other elements.
The FCC structure, characterized by its repeating pattern of atoms arranged at the corners and centers of each face of a cube, influences the properties of the element in several ways.
Physical Properties, Fcc element 3 study guide pdf
The physical properties of FCC element 3 are summarized in the table below:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 27 |
| Atomic Weight | 58.9332 |
| Melting Point | 1083°C (1981°F) |
| Boiling Point | 2562°C (4643°F) |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm³ |
The FCC structure contributes to the element’s high melting and boiling points, as the closely packed atoms require more energy to overcome the interatomic forces and break the crystal lattice.
Chemical Properties
FCC element 3 is a transition metal with a variable oxidation state, ranging from +2 to +6. It is a relatively unreactive element, but it can react with acids and bases to form salts.
The FCC structure affects the element’s chemical properties by influencing the accessibility of its valence electrons. The closely packed atoms in the FCC structure limit the mobility of valence electrons, making the element less reactive than other transition metals with a more open crystal structure.
Applications of FCC Element 3
FCC element 3 is widely employed across various industries and applications due to its unique properties, including its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures.
In the automotive industry, FCC element 3 is utilized in the production of lightweight components, such as engine blocks, pistons, and suspension systems, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and performance. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for exhaust systems and other components exposed to harsh environments.
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, FCC element 3 is employed in the construction of aircraft frames, wings, and other structural components. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows for the design of lightweight aircraft with enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced operating costs.
The fcc element 3 study guide pdf provides comprehensive information on the properties and applications of this element. If you’re looking for more in-depth knowledge about the components of a TIG welding torch, check out our article on tig welding torch parts name . This guide will help you understand the functions of each part and how they contribute to the overall performance of the torch.
Afterward, you can return to the fcc element 3 study guide pdf to continue your exploration of this fascinating element.
Construction Industry
Within the construction industry, FCC element 3 is used in the fabrication of bridges, buildings, and other structures. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosion makes it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as coastal areas or regions with extreme weather conditions.
Medical Industry
In the medical industry, FCC element 3 is utilized in the production of surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. Its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion make it suitable for long-term use in the human body.
Other Applications
Beyond these primary industries, FCC element 3 also finds applications in various other fields, including electronics, energy, and consumer products. Its unique properties make it a versatile material with a wide range of potential uses.
Manufacturing and Processing of FCC Element 3
The manufacturing and processing of FCC element 3 involve several key steps, including extraction, refining, and shaping. These processes are essential for producing the various forms of FCC element 3 used in different applications.
Extraction and Refining
FCC element 3 is typically extracted from its ores, which are found in the Earth’s crust. The extraction process involves mining the ores and separating the FCC element 3 from other minerals. This can be achieved through various methods, such as flotation, magnetic separation, or chemical leaching.
Once extracted, the FCC element 3 is further refined to remove impurities and obtain a pure form of the metal. Refining processes may include electrolysis, distillation, or zone refining, depending on the specific FCC element 3 and the desired purity level.
Shaping and Processing
After refining, FCC element 3 can be shaped and processed into various forms, such as sheets, rods, wires, or tubes. These processes involve applying heat, pressure, or mechanical force to the metal.
- Rolling:FCC element 3 can be rolled into thin sheets or strips using rolling mills. This process involves passing the metal through a series of rollers, which gradually reduce its thickness.
- Extrusion:FCC element 3 can be extruded into rods, wires, or tubes by forcing it through a die with the desired shape. This process requires high pressure and specialized equipment.
- Drawing:Wires of FCC element 3 can be drawn by pulling the metal through a series of dies with progressively smaller diameters. This process reduces the wire’s diameter and increases its length.
The manufacturing and processing of FCC element 3 are crucial steps in the production of various metal products used in industries such as electronics, construction, and transportation.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
The production, use, and disposal of FCC element 3 involve potential environmental and safety concerns that must be addressed. Regulations and guidelines are in place to minimize these risks and ensure responsible handling of the element.
Environmental Concerns
FCC element 3 can pose environmental risks if not handled properly. Its extraction and processing can release pollutants into the air and water, affecting ecosystems and human health. Additionally, improper disposal of waste containing FCC element 3 can lead to contamination of soil and groundwater.
Safety Concerns
FCC element 3 can also present safety hazards. Inhalation of its dust or fumes can cause respiratory problems, and skin contact can result in irritation or burns. Furthermore, the element is combustible and can release toxic gases when heated.
Regulations and Guidelines
To mitigate these risks, regulations and guidelines have been established to govern the production, use, and disposal of FCC element 3. These measures include:
- Emission standards for air and water pollutants
- Waste disposal protocols to prevent contamination
- Occupational safety guidelines for workers handling the element
By adhering to these regulations and guidelines, industries and individuals can minimize the environmental and safety risks associated with FCC element 3.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of FCC element 3’s crystal structure?
The FCC crystal structure of element 3 plays a crucial role in determining its properties. The face-centered cubic arrangement of atoms provides high strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
How is FCC element 3 used in various industries?
FCC element 3 finds applications in diverse industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for lightweight components in aircraft and vehicles, while its electrical conductivity makes it suitable for electrical wires and circuits.
What are the environmental and safety considerations associated with FCC element 3?
The production and use of FCC element 3 require careful consideration of environmental and safety concerns. Proper disposal methods are essential to minimize its impact on the environment, and appropriate safety measures must be taken to protect workers and the general public from potential hazards.